Pre-PhD: Would Active Labor Market Policies Help Combat High U.S. Unemployment?
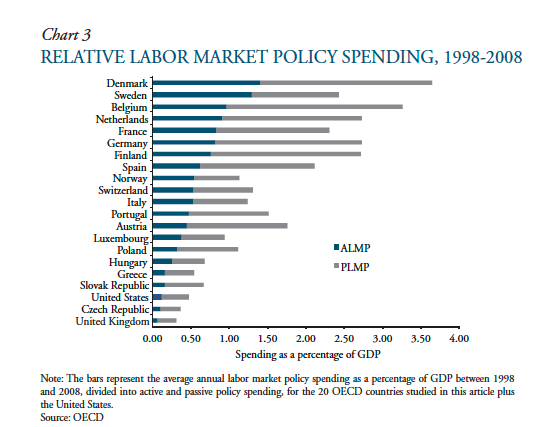
Using OECD data from 1998-2008, we estimate the effects of disaggregated types of labor market policies on unemployment. We find that training programs and job-search assistance reduce unemployment significantly. Using simple calculations based on Okun’s Law and assumptions about the productivity of newly employed workers, we show that these programs are also cost-effective: by reducing unemployment, they generate more GDP than they would cost the government to implement.